11th Standard CBSE Physics Subjects Question Paper Software Subscription
QB365 covers complete information about 11th Standard CBSE Physics Subject for 2022-2023 Exam. Question Bank includes 11th Standard CBSE Physics Subjects Book back questions, other important questions, Creative questions, Extra questions, PTA quesions, Previous Year questions and other key points also. All question with detailed answers are readily available for preparting Physics question papers.
All Chapters Covered

Create Unlimited Question Papers

Access anywhere anytime
Multiple Pattern Question Papers
Share your Question Paper
Font size, line spacing, watermark etc,
Our Other Subjects for 11th Standard CBSE
11th Standard CBSE Physics Chapters / Lessons
Physical World
Units and Measurements
Motion in a Straight Line
Motion in a Plane
Laws of Motion
Work, Energy and Power
System of Particles and Rotational Motion
Gravitation
Mechanical Properties of Solids
Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Thermal Properties of Matter
Thermodynamics
Kinetic Theory
Oscillations
Waves
11th Standard CBSE Physics Chapters / Lessons Syllabus
Physical World and Measurement
Chapter-1: Physical World
Physics-scope and excitement; nature of physical laws; Physics, technology and society.
Chapter12: Units and Measurements
Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental and derived units. Length, mass and time measurements; accuracy and precision of measuring instruments; errors in measurement; significant figures. - Dimensions of physical quantities, dimensional analysis and its applications.
Kinematics
Chapter-3: Motion in a Straight Line
Frame of reference, Motion in a straight line: Position-time graph, speed and velocity. Elementary concepts of differentiation and integration for describing motion, uniform and non-uniform motion, average speed and instantaneous velocity, uniformly accelerated motion, velocity - time and position-time graphs. Relations for uniformly accelerated motion (graphical treatment).
Chapter-4: Motion in a Plane
Scalar and vector quantities; position and displacement vectors, general vectors and their notations; equality of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a real number; addition and subtraction of vectors, relative velocity, Unit vector; resolution of a vector in a plane, rectangular components, Scalar and Vector product of vectors.
Motion in a plane, cases of uniform velocity and uniform acceleration-projectile motion, uniform circular motion.
Laws of Motion
Chapter-5: Laws of Motion
Intuitive concept of force, Inertia, Newton's first law of motion; momentum and Newton's second law of motion; impulse; Newton's third law of motion - Law of conservation of linear momentum and its applications - Equilibrium of concurrent forces, Static and kinetic friction, laws of friction, rolling friction, lubrication - Dynamics of uniform circular motion: Centripetal force, examples of circular motion (vehicle on a level circular road, vehicle on a banked road).
Work, Energy and Power
Chapter-6: Work, Engery and Power
Work done by a constant force and a variable force; kinetic energy, work-energy theorem, power - Notion of potential energy, potential energy of a spring, conservative forces: conservation of mechanical energy (kinetic and potential energies); non-conservative forces: motion in a vertical circle; elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two dimensions.
Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body
Chapter-7: System of Particles and Rotational Motion
Centre of mass of a two-particle system, momentum conservation and centre of mass motion - Centre of mass of a rigid body; centre of mass of a uniform rod - Moment of a force, torque, angular momentum, law of conservation of angular momentum and its applications - Equilibrium of rigid bodies, rigid body rotation and equations of rotational motion, comparison of linear and rotational motions - Moment of inertia, radius of gyration, values of moments of inertia for simple geometrical objects (no derivation). Statement of parallel and perpendicular axes theorems and their applications.
Gravitation
Chapter-8: Gravitation
Kepler's laws of planetary motion, universal law of gravitation - Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth - Gravitational potential energy and gravitational potential, escape velocity, orbital velocity of a satellite, Geo-stationary satellites.
Properties of Bulk Matter
Chapter-9: Mechanical Properties of Solids
Elastic behaviour, Stress-strain relationship, Hooke's law, Young's modulus, bulk modulus, shear modulus of rigidity, Poisson's ratio; elastic energy.
Chapter-10: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal's law and its applications (hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes), effect of gravity on fluid pressure - Viscosity, Stokes' law, terminal velocity, streamline and turbulent flow, critical velocity, Bernoulli's theorem and its applications - Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure across a curved surface, application of surface tension ideas to drops, bubbles and capillary rise.
Chapter-11: Thermal Properties of Matter
Heat, temperature, thermal expansion; thermal expansion of solids, liquids and gases, anomalous expansion of water; specific heat capacity; Cp, Cv - calorimetry; change of state - latent heat capacity.
Heat transfer-conduction, convection and radiation, thermal conductivity, qualitative ideas of Blackbody radiation, Wein's displacement Law, Stefan's law, Green house effect.
Thermodynamics
Chapter-12: Thermodynamics
Thermal equilibrium and definition of temperature (zeroth law of thermodynamics), heat, work and internal energy. First law of thermodynamics, isothermal and adiabatic processes - Second law of thermodynamics: reversible and irreversible processes, Heat engine and refrigerator.
Behaviour of Perfect Gases and Kinetic Theory of Gases
Chapter-13: Kinetic Theory
Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done in compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases - assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic interpretation of temperature; rms speed of gas molecules; degrees of freedom, law of equipartition of energy (statement only) and application to specific heat capacities of gases; concept of mean free path, Avogadro's number.
Oscillations and Waves
Chapter-14: Oscillations
Periodic motion - time period, frequency, displacement as a function of time, periodic functions - Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M) and its equation; phase; oscillations of a loaded spring restoring force and force constant; energy in S.H.M. Kinetic and potential energies; simple pendulum derivation of expression for its time period. Free, forced and damped oscillations (qualitative ideas only), resonance.
Chapter-15: Waves
Wave motion: Transverse and longitudinal waves, speed of wave motion, displacement relation for a progressive wave, principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, standing waves in strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and harmonics, Beats, Doppler effect.
Physical World
What is Physics-Scope and Excitement of Physics-Physics, Technology and Society-Fundamental Forces in Nature-Nature of Physical Laws
Units and Measurement
Introduction- The International System of Units-Measurement of Length-Measurement of Mass-Measurement of Time-Accuracy, Precision of Instruments and Errors in Measurement-Significant Figures-Dimensions of Physical Quantities-Dimensional Formulae and Dimensional Equations-Dimensional Analysis and its Applications
Motion in a Straight Line
Introduction-Position, Path Length and Displacement-Average Velocity and Average Speed-Instantaneous Velocity and Speed-Acceleration-Kinematic Equations for Uniformly Accelerated Motion-Relative Velocity
Motion in a Plane
Introduction-Scalars and Vectors-Multiplication of Vectors by Real Numbers-Addition and Subtraction of Vectors – Graphical Method-Resolution of Vectors-Vector Addition -Analytical Method-Motion in a Plane-Motion in a Plane with Constant Acceleration-Relative Velocity in Two Dimensions-Projectile Motion-Uniform Circular Motion
Laws of Motion
Introduction-Aristotle’s Fallacy-The Law of Inertia-Newton’s First Law of Motion-Newton’s Second Law of Motion-Newton’s Third Law of Motion-Conservation of Momentum-Equilibrium of A Particle-Common Forces in Mechanics-Circular Motion-Solving Problems in Mechanics
Work, Energy and Power
Introduction-Notions of Work and Kinetic Energy: The Work-Energy Theorem-Work-Kinetic Energy-Work Done by a Variable Force-The Work-Energy Theorem for a Variable Force-The Concept of Potential Energy-The Conservation of Mechanical Energy-The Potential Energy of a Spring-Various Forms of Energy: The Law of Conservation of Energy-Power-Collisions
System of Particles and Rotational Motion
Introduction-Centre of Mass-Motion of Centre of Mass-Linear Momentum of a System of Particles-Vector Product of Two Vectors-Angular Velocity and its Relation With Linear Velocity-Torque and Angular Momentum-Equilibrium of a Rigid Body-Moment of Inertia-Theorems of Perpendicular and Parallel Axes-Kinematics of Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis-Dynamics of Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis-Angular Momentum in Case of Rotations about a Fixed Axis-Rolling Motion
Gravitation
Introduction-Kepler’s Laws-Universal Law of Gravitation-The Gravitational Constant-Acceleration Due to Gravity of The Earth-Acceleration Due to Gravity Below and Above The Surface of Earth-Gravitational Potential Energy-Escape Speed-Earth Satellite-Energy of an Orbiting Satellite-Geostationary and Polar Satellites-Weightlessness
Mechanical Properties of Solids
Introduction-Elastic Behaviour of Solids-Stress and Strain-Hooke’s Law-Stress-Strain Curve-Elastic Moduli-Applications of Elastic Behaviour of Materials
Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Introduction-Pressure-Streamline Flow-Bernoulli’s Principle-Viscosity-Reynolds Number-Surface Tension
Thermal Properties of Matter
Introduction-Temperature and heat-Measurement of temperature-Ideal-Gas Equation and Absolute Temperature-Thermal Expansion-Specific Heat Capacity-Calorimetry-Change of State-Heat Transfer-Newton’s Law of Cooling
Thermodynamics
Introduction-Thermal Equilibrium-Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics-Heat, Internal Energy and Work-First Law of Thermodynamics-Specific Heat Capacity-Thermodynamic State Variables and Equation of State-Thermodynamic Processes-Heat Engines-Refrigerators and Heat Pumps-Second Law of Thermodynamics-Reversible and Irreversible Processes-Carnot Engine
Kinetic Theory
Introduction-Molecular Nature of Matter-Behaviour of Gases-Kinetic Theory of an Ideal Gas-Law of Equipartition of Energy-Specific Heat Capacity-Mean Free Path
Oscillations
Introduction-Periodic and Oscillatory Motions-Simple Harmonic Motion-Simple Harmonic Motion and Uniform Circular Motion-Velocity and Acceleration in Simple Harmonic Motion-Force Law for Simple Harmonic Motion-Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion-Some Systems Executing Simple Harmonic Motion-Damped Simple Harmonic Motion-Forced Oscillations and Resonance
Waves
Introduction-Transverse and Longitudinal Waves-Displacement Relation in a Progressive Wave-The Speed of a Travelling Wave-The Principle of Superposition of Waves-Reflection of Waves-Beats-Doppler Effect
Features in Question Paper Preparation software

(or) type Question

Add or Remover

Sub Questions
Adding Notes

Multiple Pattern

All subjects available
How to Create 11th Standard CBSE Physics Question Paper
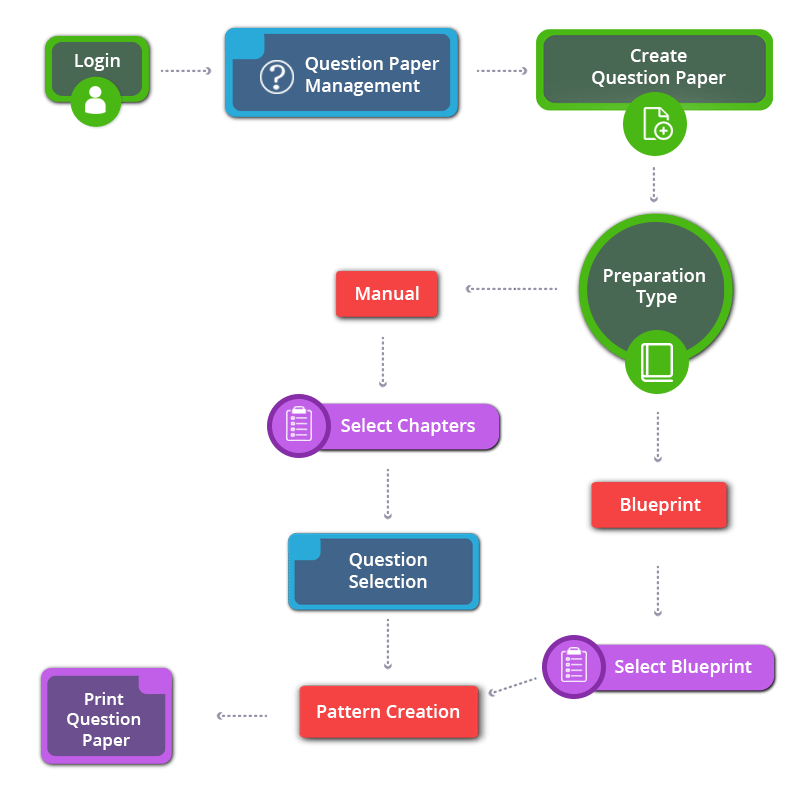

11th Standard CBSE Physics
- Covers all chapters
- Unique Creative Questions
- Unlimited Question Paper
- Multiple Patterns & Answer keys
4600
4140



