Class 10th Science - Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10 Science Subject - Chemical Reactions and Equations, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions With Answer Key
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
Chemical equation is a method of representing a chemical reaction with the help of symbols and formulae of the substances involved in it. In a chemical equation, the substances which combine or react are called reactants and new substances produced are called products. A chemical equation is a short hand method of representing a chemical reaction. A balanced chemical equation has equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products side. An unbalanced chemical equation has unequal number of atoms of one or more elements in reactants and products. Formulae of elements and compounds are not changed to balance an equation.
(i) Consider the following reaction:
pMg3N2 + qH2O ⇾ rMg(OH)2 + sNH3
When the equation is balanced, the coefficients p, q, r, s respectively are(a) 1,3,3,2 (b) 1,6,3,2 (c) 1,2,3,2 (d) 2,3,6, 2 (ii) Which of the following information is not conveyed by a balanced chemical equation?
(a) Physical states of reactants and products (b) Symbols and formulae of all the substances involved in a particular reaction (c) Number of atoms/molecules of the reactants and products formed (d) Whether a particular reaction is actually feasible or not (iii) The balancing of chemical equations is in accordance with
(a) law of combining volumes (b) law of constant proportions (c) law of conservation of mass (d) both (b) and (c) (iv) Which of the following chemical equations is an unbalanced one?
\( { (a) } 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) \({ (b) } 2 \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{10}+12 \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 8 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+10 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) \(\text {(c) } 2 \mathrm{Al}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{Al}(\mathrm{OH})_{3}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2}\) \(\text { (d) } 4 \mathrm{NH}_{3}+5 \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 4 \mathrm{NO}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) (v) Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(a) A chemical equation tells us about the substances involved in a reaction. (b) A chemical equation informs us about the symbols and formulae of the substances involved in a reaction. (c) A chemical equation tells us about the atoms or molecules of the reactants and products involved in a reaction. (d) All the above (a) -
In decomposition reactions, a single reactant breaks down to form two or more products. A decomposition reaction is opposite to combination reaction. Thermal decomposition reactions use the energy in form of heat for the decomposition of reactants. Electrolytic decomposition reactions involve the use of electrical energy for the decomposition of reactant molecules. Photolysis or photochemical decomposition involves the use of light energy for the purpose of decomposition.
(i) Which of the following reactions is a decomposition reaction?\({ (a) \ } \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{HCl} \longrightarrow \mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) \({ (b) \ } \mathrm{NH}_{4} \mathrm{CNO} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{NCONH}_{2}\) \({ (C) \ } 2 \mathrm{KCIO}_{3} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{KCl}+3 \mathrm{O}_{2}\) \( { (d) \ } \mathrm{H}_{2}+\mathrm{I}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{HI}\) \({ (ii) \ } 2 \mathrm{~Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{PbO}+n A+\mathrm{O}_{2}\)
What is nA in the given reaction?(a) 4NO (b) 4NO2 (c) 2PbNO2 (d) NO2 (iii) Amino acid is formed by the decomposition of which component of our diet?
(a) Carbohydrate (b) Starch (c) Protein (d) Fat (iv) Silver chloride on exposure to sunlight for a long duration turns grey due to
(I) the formation of silver by decomposition of silver chloride
(II) sublimation of silver chloride
(III) decomposition of chlorine gas from silver chloride
(IV) oxidation of silver chloride
The correct statement(s) is/are(a) Only (I) (b) Only (II) and (III) (c) Only (I) and (II) d) Only (IV) (v) What type of chemical reaction takes place when electricity is passed through water?
(a) Thermal decomposition (b) Electrolytic decomposition (c) Photochemical decomposition (d) Displacement reaction (a) -
Redox reactions are those reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur Simultaneously. A redox reaction is made up of two half reactions. In the first half reaction, oxidation takes place and in second half reaction, reduction occurs. Oxidation is a process in which a substance loses electrons and in reduction, a substance gains electrons. The substance which gains electrons is reduced and acts as an oxidising agent. On the other hand, a substance which loses electrons is oxidised and acts as a reducing agent.
(i) Which of the following is a redox reaction?\({ (a) \ } \mathrm{CaCO}_{3} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaO}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{H}_{2}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{HCl}\) \({ (c) \ } \mathrm{CaO}+2 \mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaCl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) \(\text { (d) } \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) (ii) Identify the reaction in which H2 02 is acting as a reducing agent.
\(\text { (a) } \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) \(\text { (b) } 2 \mathrm{Hl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{I}_{2}\) \(\text { (c) } \mathrm{Cl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{O}_{2}\) \(\text { (d) } 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{3}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) (iii) For the following reactions, identify the one in which H2S acts as a reducing agent.
\(\text { (a) } \mathrm{CuSO}_{4}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CuS}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}\) \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{Cd}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CdS}+2 \mathrm{HNO}_{3}\) \(\text { (c) } 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{S}\) (d) None of these (iv) For the following reaction, identify the correct statement.
\(\mathrm{ZnO}+\mathrm{CO} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\)(a) ZnO is being reduced. (b) CO2 is being oxidised (c) CO is being reduced. (d) ZnO is being oxidised. (v) In the following reaction, which substance is reduced?
\(\mathrm{PbS}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbSO}_{4}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)(a) H2O (b) H2 O2 (c) PbS d) PbSO4 (a) -
In a balanced chemical reaction, equal number of atoms are present on both sides of reaction. A balanced chemical reaction is based on law of conservation of mass which means that total mass of reactants and products participating in a reaction must be equal. For example, a balanced chemical equation of burning of magnesium in oxygen to form magnesium oxide is written as :
\(2 \mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{MgO}\)
The mass of reactants (2 x 24 + 32 = 80) is equal to the mass of products [2 x (24 + 16) = 80]
(i) In a reaction, 35 g of reactant, PQ breaks down into 20 g of product, P and an unknown amount of product, Q. Using the law of conservation of mass, weight of products, Q will be(a) 25g (b) 35g (c) 30g (d) 15g (ii) When solid mercury (II) oxide is heated, liquid mercury and oxygen gas are produced. Which of the following statements is true regarding the balanced chemical equation for this process?
(a) 1 mole of mercury (II) oxide produces two moles of mercury and one mole of oxygen gas
(b) 2 moles of mercury (II) oxide produce one mole of mercury and one mole of oxygen gas
(c) 1 mole of mercury (II) oxide produces half mole of mercury and half mole of oxygen gas
(d) 2 moles of mercury (II) oxide produce 2 moles of mercury and one mole of oxygen gas
(iii) Which of the following laws is satisfied by a balanced chemical equation?(a) Law of multiple proportions (b) Law of conservation of mass (c) Law of conservation of motion (d) Law of conservation of magnetism (iv) In the given chemical reaction
\(\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{6(l)}+15 \mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow m \mathrm{CO}_{2(g)}+n \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)}\)
The values of m and n are respectively(a) 14 and 8 (b) 12 and 6 (c) 8 and 10 (d) 12 and 10 (v) Sulphur dioxide reacts with oxygen to form sulphur trioxide. What would be the molar ratio of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide?
(a) 2: 3 (b) 1: 1 (c) 1: 2 (d) 3: 2 (a) -
In a chemical reaction, reactants are converted into products. The conversion of reactants into products in a chemical reaction is often accompanied by some features which can be observed easily. These easily observed features which take place as a result of chemical reaction are known as characteristics of chemicals reactions. Some important characteristics of chemical reactions are:
(I) Evolution of heat
(II) Formation of precipitate
(III) Change in colour
(IV) Change in temperature
(V) Change in state
Anyone of these general characteristics can tell us whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not.
(i) Reaction of magnesium with air is a/an(a) exothermic reaction (b) endothermic reaction (c) reversible reaction (d) substitution reaction (ii) In the following reaction
\(\mathrm{Ca}_{(a q)}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{OH}_{(a q)}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2(s)}\)
precipitate of calcium hydroxide will be of(a) green colour (b) blue colour (c) brown colour (d) white colour (iii) In the given reaction,
\(\mathrm{S}_{(s)}+\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{SO}_{2}\)
the physical state of SO2 is(a) liquid (b) solid (c) gaseous (d) all three (iv) Which one of the following processes involve chemical reactions?
(a) Storing of oxygen gas under pressure in a gas cylinder. (b) Keeping petrol in a china dish in the open. (c) Liquefaction of air. (d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature. (v) In which of the following reactions, high amount of heat energy will be evolved?
(a) Electrolysis of water (b) Dissolution of NH4Cl in water (c) Burning of L.P.G. (d) Decomposition of AgBr in the presence of light (a) -
A reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product is called a combination reaction. For example, calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form calcium hydroxide. The reaction is highly exothermic in nature, as lots of heat is produced during the reaction.
\(\mathrm{CaO}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2(a q)}+\text { Heat }\)
Calcium oxide Water Calcium hydroxide
Solution of Ca(OH)2 is used for white wash the walls. Calcium hydroxide reacts slowly with carbon dioxide in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate on the wall which gives a shiny appearance to wall. Calcium carbonate will form after two or three days of white wash.
(i) What is the chemical name of quick lime?(a) Calcium oxide (b) Calcium carbonate (c) Calcium hydroxide (d) Carbon dioxide (ii) When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water,
(a) calcium hydroxide is formed (b) white precipitate of CaO is formed (c) lime water turns milky (d) colour of lime water becomes green. (iii) Following observations are observed when calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water.
Identify the incorrect observations
(I) It is an endothermic reaction (II) Slaked lime is produced.
(III) Quick lime is produced. (IV) It is an exothermic reaction.
(V) It is a combination reaction(a) (I) and (II) (b) (III) and (IV) (c) (I) and (III) (d) (II), (IV) and (V) (iv) Quick lime combines Vigorously with water to form (A) which reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide in air to form (B)
Identify the compounds(A) and (B)(A) (B) (a) Calcium carbonate Calcium hydroxide (b) Calcium hydroxide Calcium carbonate (c) Calcium Calcium bicarbonate (d) Calcium bicarbonate Calcium (v) Among the following, the endothermic reaction is
(a) combination of carbon and oxygen to form carbon monoxide (b) combination of nitrogen and oxygen to form nitrogen monoxide (c) combination of glucose and oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water (d) combination of zinc and hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen (a) -
Reactions in which one element takes place of another element in a compound, are known as displacement reactions. In general, more reactive elements displaces a less reactive element from its compound. In all single displacement reactions, only one element displaces another element from its compound. The single displacement reactions are, however, written as just displacement reactions. The displacement reaction between iron (III) oxide and powdered aluminium produces so much heat that iron metal obtained is in molten form.
(i) Copper displaces which of the following metals from its salt solution?(a) ZnSO4 (b) FeSO4 (c) AgNO3 (d) NiSO4 (ii) When zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, the gas evolved is
(a) red in colour and have a sweet smelling (b) green in colour and have a foul smell (c) colourless, odourless and burns with a pop sound (d) colourless, pungent smelling and burns with a pop sound (iii) When dry hydrogen is passed over a heated oxide of metal X using the apparatus shown below, a reddish-brown residue is obtained
The reddish -brown residue could be(a) copper (b) lead (c) silver (d) zinc (iv) Which of the following reactions is a displacement reaction?
\(\text { (a) } \mathrm{CaO}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2}\) \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{MgCO}_{3} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) \(\text { (c) } \mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{CuSO}_{4} \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgSO}_{4}+\mathrm{Cu}\) \(\text { (d) } \mathrm{H}_{2}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{HCl}\) (v) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to granulated zinc placed in a test tube, the observation made is
(a) the surface of the metal turns shining (b) the reaction mixture turns milky (c) greenish yellow gas is evolved (d) the colourless and odourless gas evolves with a pop sound. (a) -
Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions. A double displacement reaction usually occurs in solution and one of the products, being insoluble, precipitate out (separates as a solid). Any reaction in which an insoluble solid (called precipitate) is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction. The reaction in which acid or acidic oxide reacts with base or basic oxide to form salt and water is called neutralisation reaction.
For example, \(2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
(i) When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a(a) combination reaction (b) displacement reaction (c) decomposition reaction (d) double displacement reaction (ii) Which of the following is not a double displacement reaction?
\(\text { (a) } \mathrm{AgNO}_{3(a q)}+\mathrm{NaCl}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{AgCl}_{(s)}+\mathrm{NaNO}_{3(a q)}\) \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{Zn}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{ZnSO}_{4(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2(g)}\) \(\text { (c) } \mathrm{CuSO}_{4(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CuS}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)}\) \(\text { (d) } \mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2(a q)}+2 \mathrm{KI}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbI}_{2(s)}+2 \mathrm{KNO}_{3(a q)}\) (iii) Barium chloride on reaction with ammonium sulphate forms barium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Which of the following correctly represents the type of the reaction involved?
(I) Displacement reaction
(II) Precipitation reaction
(III) Combination reaction
(IV) Double displacement reaction(a) (I) only (b) (II) only (c) (III) and (IV) only (d) (II) and ( V) only (iv) Identify A in the following reaction.
\(\mathrm{AlCl}_{3(a q)}+3 \mathrm{NH}_{4} \mathrm{OH}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow A+3 \mathrm{NH}_{4} \mathrm{Cl}_{(a q)}\)(a) AI(OH)3 (b) Al2 O3 (c) AIH3 (d) AIN (v) Consider the following reaction,
\(\mathrm{BaCl}_{2}+\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} \longrightarrow \mathrm{BaSO}_{4}+2 \mathrm{NaCl}\)
identify the precipitate in the reaction,(a) BaCl2 (b) BaSO4 (c) Na2sO4 (d) NaCI (a) -
The earlier concept of oxidation and reduction is based on the addition or removal of oxygen or hydrogen elements so, in terms of oxygen and hydrogen, oxidation is addition of oxygen to a substance and removal of hydrogen from a substance. On the other hand, reduction is addition of hydrogen to a substance and removal of oxygen from a substance. The substance which gives oxygen to another substance or removes hydrogen from another substance in an oxidation reaction is known as oxidising agent, while the substance which gives hydrogen to another substance or removes oxygen from another substance in a reduction reaction is known as reducing agent. For example,
(i) A redox reaction is one in which(a) both the substances are reduced (b) both the substances are oxidised (c) an acid is neutralised by the base (d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced. (ii) In the reaction, \(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{S}+2 \mathrm{HCl}\)
(a) H2S is the reducing agent. (b) HCI is the oxidising agent. (c) H2S is the oxidising agent. (d) Cl2 is the reducing agent. (iii) Which ofthe following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) Formation of slaked lime from quick lime. (b) Heating mercuric oxide. (c) Formation of manganese chloride from manganese oxide (MnO2). (d) Formation of zinc from zinc blende. \(\text { (iv) } \mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{CuO} \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgO}+\mathrm{Cu}\)
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
(a) CuO gets reduced (b) Mg gets oxidised. (c) CuO gets oxidised. (d) It is a redox reaction. (v) Identify the correct oxidising agent and reducing agent in the following reaction.
\(\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}+2 \mathrm{Al} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{Fe}+\mathrm{Al}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}\)(a) AI- Oxidising agent, Fe2O3 - Reducing agent (b) Fe2 O3 - Oxidising agent, AI- Reducing agent (c) Fe - Oxidising agent, Al2O3 - Reducing agent (d) Fe2O3 - Oxidising agent, Al2O3 - Reducing agent (a) -
Oxidation has damaging effect on metals as well as on food. The damaging effect of oxidation on metal is studied as corrosion and that on food is studied as rancidity. The phenomenon due to which metals are slowly eaten away by the reaction of air, water and chemicals present in atmosphere, is called corrosion. For example, iron articles are shiny when new, but get coated with a reddish brown powder when left for sometime. This process is known as rusting of iron. Rancidity is the process of slow oxidation of oil and fat (which are volatile in nature) present in the food materials resulting in the change of smell and taste in them.
(i) Rancidity can be prevented by(a) adding antioxidants (b) packaging oily food in nitrogen gas (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these. (ii) Combination of phosphorus and oxygen is an example of
(a) oxidation (b) reduction (c) rancidity (d) none of these (iii) A science teacher wrote the following statements about rancidity :
(I) When fats and oils are reduced, they become rancid.
(II) In chips packet, rancidity is prevented by oxygen.
(III) Rancidity is prevented by adding antioxidants.
Select the correct option.(a) (I) only (b) (II) and (III) only (c) (III) only (d) (I), (II), and (III) (iv) Two statements are given below regarding rusting of iron.
(I) The rusting of iron is a redox reaction and reaction occurs as, \(4 \mathrm{Fe}+3 \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 4 \mathrm{Fe}^{3+}+6 \mathrm{O}^{2-}\)
(II) The metallic iron is oxidised to \(\mathrm{Fe}^{2+} \text { and } \mathrm{O}_{2} \text { is reduced to } \mathrm{O}^{2-}\)
Select the correct statement(s).(a) I only (b) II only (c) Both I and II (d) None of these (v) Which of the following measures can be adopted to prevent or slow down rancidity?
(I) Food materials should be packed in air tight container.
(II) Food should be refrigerated.
(III) Food materials and cooked food should be kept away from direct sunlight(a) Only II and III (b) Only I and III (c) Only II and III (d) I, II and III (a) -
Chemical reaction, a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the products. Substances are either chemical elements or compounds. A chemical reaction rearranges the constituent atoms of the reactants to create different substances as products. Study this table related to the different types of reactions / processes and answer the questions that follow.
S.No. Name of Process Word Equation i Combustion \(\text { Magnesium }+\text { Oxygen } \stackrel{\text { heat }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Magnesium dioxide }\) ii Photosynsthesis \(\text { Carbon dioxide }+\text { Water } \frac{\text { sunlight }}{\text { chlorophyll }} \longrightarrow \text { Glucose }+\text { Oxygen }+\text { Water }\) iii Combination \(\text { Iron }+\text { Sulphur } \stackrel{\text { heat }}{\rightarrow} \text { Iron sulphide }\) iv. Photodecomposition \(\text { Silver bromide } \stackrel{\text { light }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Silver }+\text { Bromine }\) (i) The reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance under suitable conditions is
(a) combination reaction (b) combustion
(c) decomposition reaction (d) photosynthesis
(ii) Which of the following is essential for photosynthesis?
(a) Sunlight (b) Chlorophyll (c) Glucose (d) Both 'a' and 'b’
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesis nutrients from carbon dioxide and water.
(iii) When a chemical compound decomposes on absorbing light and energy, then the reaction which takes place is known as
(a) photosynthesis (b) photodecomposition
(c) combination (d) thermal decomposition.
A photodecomposition is a chemical reaction in which an inorganic chemical (or an organic chemical) is broken down by photons and is the interaction of one or more photons with one target molecule.
(iv) Which of the following reactions is an example of combustion reaction ?
\((a) \mathrm{C}_{(s)}+\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2(g)}\\ (b) \mathrm{Zn}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{ZnSO}_{4(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2(g)}\\ (c) \mathrm{Zn}_{(s)}+2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{ZnCl}_{2(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2(g)}\\ (d) 3 \mathrm{Mg}_{(s)}+\mathrm{N}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Mg}_{3} \mathrm{~N}_{2(s)}\)
A combustion reaction is a reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy in the form of light and heat.
(v) Which of the following is an example of combination reaction?
\((a) \mathrm{H}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2(g)} \stackrel{\text { light }}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(g)}\\ (b) \mathrm{Fe}_{(s)}+S_{(s)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{FeS}_{(g)}\\ (c) 2 \mathrm{H}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)}\\ (d) All \ of \ them\)
A combination reaction (also known as a synthesis reaction) is a reaction where two or more elements or compounds (reactants) combine to form a single compound (product).(a) -
In the below experiment, when an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, a brown coating of copper is formed in the surface of iron and the colour of copper sulphate solution changes from blue to pale green. The reaction shows that iron is more reactive than copper because it displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution.
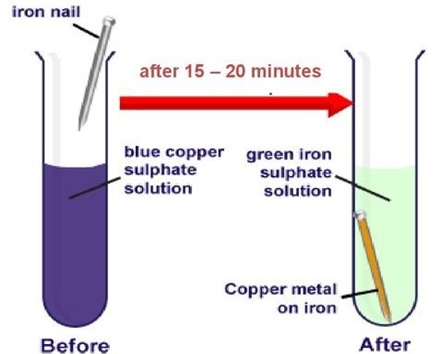
(i) The equation \(\mathrm{Cu}+\mathrm{xHNO}_{3} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2}+\mathrm{yNO}_{2}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
The values of x and y are
(a) 3 and 5 (b) 8 and 6 (c) 4 and 2 (d) 7 and 1
(ii) What happens when copper rod is dipped in iron sulphate solution :
(a) Copper displaces iron
(b) Blue colour of copper sulphate solution is obtained
(c) No reaction takes place
(d) Reaction is exothermic
(iii) A substance which oxidised itself and reduces other is known as :
(a) Oxidising agent (b) Reducing agent (c) Both (a) and (b) (d) None of these
(iv) \(\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}+2 \mathrm{Al} \rightarrow \mathrm{Al}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}+2 \mathrm{Fe}\)
The above reaction is an example of a :
(a) Combination reaction (b) Double displacement reaction
(c) Decomposition reaction (d) Displacement reaction
(v) Name the products formed when iron filings are heated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) Fe (III) chloride and water
(b) Fe (II) chloride and water
(c) Fe (II) chloride and hydrogen gas
(d) Fe (III) chloride and hydrogen gas(a) -
Rahul is a skilled painter. He mixed a white coloured powder, compound X with water. The compound X reacted vigorously with water to produce a compound Y and a large amount of heat. Then, Rahul used the compound Y for white washing the walls. Customer was not satisfied with the work of Rahul as walls were not shining. But Rahul guaranteed him that the walls would shine after 2-3 days. And after 3 days of whitewash, the walls became shiny.
(i) Name the compound X, that Ramesh mixed with water.
(a) Calcium (b) Calcium oxide (c) Calcium carbonate (d) Calcium hydroxide
(ii) Name the compound Y that Ramesh got after mixing X with water.
(a) Calcium (b) Calcium oxide (c) Calcium carbonate (d) Calcium hydroxide
(iii) What type of reaction is occurred here?
(a) Decomposition reaction (b) Displacement reaction
(c) Double displacement reaction (d) Combination reaction
(iv) Which of the following reactions is responsible for shiny finish of the walls?
\((a) \ \mathrm{CaO}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2}\\ (b) \ \mathrm{Ca}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaCO}_{3}\\ (c) \ \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaCO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\\ (d) \ \mathrm{CaCO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\)
(v) Which of the following reactions is responsible for shiny finish of the walls?
(a) CaCO3 (b) CaO (c) Ca(OH)2 (d) Ca(a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers