CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Molecular Basic of Inheritance Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Molecular Basic of Inheritance Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
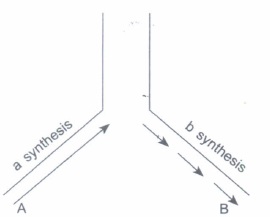
A DNA replication fork is shown above. Answer the following questions based on that.
(i) Why does DNA replication occur in such small forks?
(ii) What is a synthesis and b synthesis?
(iii) Mention the polarity at A and B.(a) -
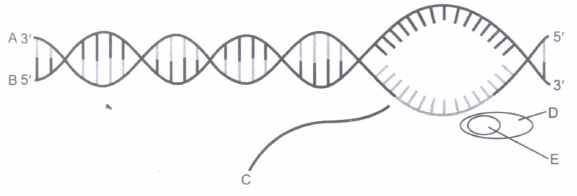
A particular stage in the transcription of a bacterium is given above. Answer the following questions:
(a) Name the stage in the process.
(b) Identify A, B, C, D and E in the diagram.(a) -
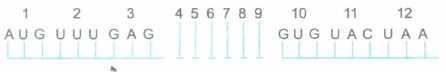
A hypothetical mRNA with 12 codons is shown above.
(a) How many amino acids will be coded by this? Justify your answer.
(b) Mention the dual functions of the codon, AUG.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
In prokaryotes, DNA is circular and present in the cytoplasm but in eukaryotes, DNA is linear and mainly confined to the nucleus. DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a long polymer of nucleotides. In 1953, the first correct double helical structure of DNA was worked out by Watson and Crick. Based on the X-ray diffraction data produced by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin. It is composed of three components, i.e., A phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar and a nitrogenous base. Different forms of DNA are B-DNA, Z-DNA, A-DNA, C-DNA and D-DNA.
(i) Name the linkage present between the nitrogen base and pentose sugar in DNA.(a) Phosphodiester bond (b) Glycosidic bond (c) Hydrogen bond (d) None of these (ii) The double helix structure of DNA was proposed by
(a) James Watson and Francis Crick (b) Earwin Chargaff (c) Federick Griffith (d) Hershey and Chase (iii) The double chain of B-DNA is coiled in a helical fashion. The spiral twisting of B-DNA duplex produces
(a) right and left part (b) major and minor grooves (c) upper and lower sides (d) linear and circular part. (iv) Assertion: The two strands of DNA helix have uniform distance between them.
Reason: A large sized purine always paired opposite to a small sized pyrimidine.(a) Both assertion and reason are true and
reason is the correct explanation of assertion.(b) Both assertion and reason are true but
reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.(c) Assertion is true but reason is false. (d) Both assertion and reason are false. (v) Which of the following describes the structure of B-DNA?
Polynucleotide chains Number of base pairs per complete turn of helix (a) Parallel 5 (b) Anti-parallel 10 (c) Parallel 15 (d) Anti-parallel 20 (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
The process of translation requires transfer of genetic information from a polymer of nucleotides to synthesise a polymer of amino acids. The relationship between the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide and nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA is called genetic code. George Gamow suggested that in order to code for all the 20 amino acids, code should be made up of three nucleotides.
(i) What is a codon?(a) A length of DNA which codes for a particular protein (b) A part of the tRNA molecule to which a
specific amino acid is attached.(c) A part of the tRNA molecule which recognises the
triplet code on the messenger RNA.(d) A part of the messenger RNA molecule that has
a sequence of bases coding for an amino acid.(ii) Three consecutive bases in the DNA molecule provide the code for each amino acid in a protein molecule. What is the maximum number of different triplets that could occurs ?
(a) 16 (b) 20 (c) 24 (d) 64 (iii) Listed below are some amino acids and their corresponding mRNA triplets.
Amino acid mRNA triplet Phenylalanine UUU Lysine AAG Arginine CGA Alanine GCA Which DNA sequence would be needed to produce the following polypeptide sequence? Alanine- Arginine- Lysine- Phenylalanine
(a) CGT GCT TTC AAA (b) CGT GCT TTC TTT (c) CGU GCU UUC AAA (d) CGU GCU UUC TTT (iv) Identify the non-sense codons among the following.
(a) AUG (b) GUG (c) UAA (d) UGG (v) A polypeptide is made using synthetic mRNA molecules as shown.
Synthetic mRNA used Polypeptide produced UUUAAAUUUAAA Phenylalanine-lysine- phenylalanine-lysine What are the DNA codes for the amino acids phenylalanine and lysine?
Phenylalanine Lysine (a) AAA TTT (b) AAA UUU (c) GGG CCC (d) TTT GGG (a)
Case Study Questions
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Molecular Basic of Inheritance Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) Replication of DNA occurs in small replication forks, because DNA is such a long molecule that the separation of the two strands along its entire length requires a very high amount of energy.
(ii) a - Continuous synthesis.
b - Discontinuous synthesis
(iii) A - 5'
B-3'. -
(a) 'Termination of transcription.
(b) A - Template strand of DNA.
B - Coding strand of DNA.
C - RNA synthesised
D - RNA-polymerase
E - rho (p) factor. -
(a) 11 amino acids will be coded, as the last codon is a termination codon that does not code for any amino acid.
(b) Dual functions of AVG:
(i) It acts as the initiation codon for translation.
·(ii) It codes for the amino acid, methionine. -
(i) (b): In DNA the nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar joins to form nucleoside with the help of bond called glycosidic bond or N-glycosidic linkage.
(ii) (a): The correct structure of DNA was first worked out by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. Their double-helix model of DNA structure was based on two major investigations, i.e., Chargaff's rules of base i'airing and study of X-ray diffraction pattern of DNA produced by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin which helped Watson and Crick to design the 3-dimensional structure of DNA.
(iii) (b): Due to spiral twisting, the B-DNA duplex comes to have two types of alternate grooves, i.e., majo: (length 22 Â) and minor (length 12 Â).
(iv) (a)
(v) (b): The double helical chains of B-DNA are bound to each other via hydrogen bonds in an antiparallel fashion, i.e., 5'-3' in one and 3'-5' in other. The pitch of helix per turn is 3.4 nm with 10 base pairs in each turn. -
(i) (d): Codon is complementary to a triplet of templet strand. It is found in mRNA. Anticodon is complementary to a codon it occurs in tRNA.
(ii) (d) : The triplet code consists of three of the four nucleotide bases - A, C, G or T. Thus the maximum number of codon is 43 = 64.
(iii) (b): The complementary bases of GCA-CGAAAG- UUU are CGT-GCT-TTC-AAA on the DNA strand.
(iv) (c): AUG and GUG are initiation codon which codes for methionine and valine respectively: UGG codes for tryptophan. UAA (ochre) is a termination codon.
(v) (a): The triplet codon of phenylalanine (UUU) ")Willbase pair with AAA in the DNA molecule and that oflysine (AAA) will base pair with TTT.
Case Study Questions






































