CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Principles of Inheritance and Variation Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Principles of Inheritance and Variation Case Study Questions 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
ABO blood group character in human population exhibits four possible phenotypes and six different genotypes. Explain the different mechanisms of inheritance involved in exhibiting the possibility of four phenotypes and six genotypes.
(a) -
Study the pedigree chart given below showing the inheritance pattern of a human trait and answer the questions that follow:
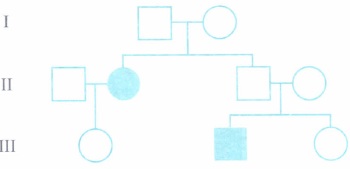
(a) Is the trait autosomal dominant or recessive or sex-linked? Why?
(b) Give the genotypes of the parents in generation I and of the son in generation II.
(c) Give the genotype of the first grand daughter.(a) -
Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disorder in humans. The pedigree chart given below shows the inheritance pattern of haemophilia in a family. Study the inheritance pattern and answer the questions that follow:
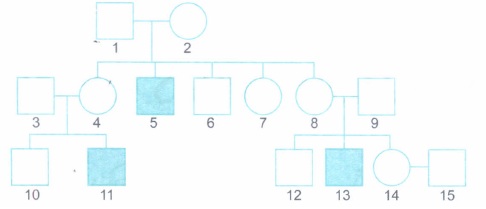
(a) Give the possible genotypes of the members 4 and 5 in the above chart.
(b) A blood test shows that the member 14 is a carrier of haemophilia. The member 15 has recently married the member 14. What is the probability of their first child being haemophilic? Show it with the help of a Punnett square.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
A relevant portion of \(\beta\)-chain of haemoglobin of a normal human is as follows
The codon for the sixth amino acid is GAG. The sixth codon GAG mutates to GAA as a result of mutation X and into GUG as a result of mutation Y.
(i) Which of the following is incorrect statement?(a) Mutation X carries no change in shape of red blood cells. (b) Mutation Y causes change in shape of red blood cell shape (c) Both mutations X and Y causes change in shape of red blood cell shape. (d) Both (a) and (b) (ii) Due to mutation Y the shape of RBCs under oxygen tension will be
(a) biconcave disc like (b) elongated and curve (c) circular (d) spherical (iii) GUG is code for
(a) valine (b) proline (c) glutamic acid (d) leucine (iv) Which of the following genotype shows diseased phenotype due to mutation Y?
(a) Hbs Hbs (b) HbA Hbs (c) HbA HbA (d) Both (a) and (b) (v) Study the given pedigree chart for sickle-cell anaemia and select the most appropriate option for the genotypes.
Genotypes of parents Genotypes of 1st and 3rd child in F1 (a) HbA HbS, HbA HbA HbA HbA, HbA HbS (b) HbA HbS, HbA HbS HbA HbA, HbA HbA (c) HbA HbA, HbA HbS HbA HbA, HbS HbS (d) HbA Hbs, HbA Hbs HbA HbS, HbS HbS (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
While studying inheritance of characters, a teacher gave the example of inheritance of attached earlobe and hypertrichosis of the ear to her students. A man with attached earlobes and extensive hair on pinna married a woman having free earlobes. The couple had four children, one son with attached earlobes and hairy pinna, one son with a free earlobes and hairy pinna and two daughters with attached earlobes. One of the daughters married a man with free earlobes and sparse hair on pinna. Teacher said if this couple would have sons there would be equal chances for both having free or attached earlobes and sparse hair on pinnae.
(i) Attached and free earlobe are respective example of(a) dominant and recessive traits (b) recessive and recessive traits (c) recessive and dominant traits (d) dominant and dominant traits. (ii) Hypertrichosis of the ear is
(a) X linked trait (b) Y linked trait (c) autosomal dominant trait (d) autosomal recessive trait (iii) If a female with attached earlobe married a male homozygous for free earlobe sparse hair on pinna then what would be the chances of daughter to have attached earlobe?
(a) 0% (b) 100% (c) 25% (d) 75% (iv) If a man with attached earlobe and hairy pinna married a woman with attached earlobe then what would be the chances of son to have hairy pinna?
(a) 50% (b) 100% (c) 75% (d) 0% (v) A male with attached earlobe, sparse hair on pinna married a female with attached earlobe. Which of the following is correct regarding their progenies?
(a) All sons have a free earlobe with hairy pinna. (b) All daughters have an attached earlobe (c) 50% daughters have an attached earlobe whereas 50% daughters have a free earlobe. (d) 50% sons have attached earlobe with hairy pinna and 50% sons have a free earlobe. (a)
Case Study Questions
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Principles of Inheritance and Variation Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
Mechanisms of Inheritance.
(i) Multiple allelism.
(a) The gene I controlling blood group character exists in three allelic forms, lA, IB and i.
(ii) Dominance.
(a) The allele IA is dominant over the allele i and the allele IB is also dominant over the allele, i.
(iii) Codominance.
(a) The alleles IA and IB are equally dominant and both of them express themselves, when they are present together; blood group AB results. -
(a) It is an autosomal recessive trait.
(i) The trait that is hidden in the parents (generation 1) has appeared in the daughter (generation II).
(b) (i) Parents - Mother Aa, Father Aa
(ii) Son (generation II) - Aa.
(c) First grand daughter - Aa. -
(a) Genotype of 4 - XXh
Genotype of 5 - xhv.

T4e probability of their first child being haemophilic is 25 per cent. -
(i) (C) : Due to mutation X, GAG mutates to GAA. But both GAG and GAA code for glutamic acid and hence there is no change in shape of RBC whereas in mutation Y, GUG is substituted by GAA that codes for valine and so the RBCs become sickle shaped.
(ii) (b) : Mutation Y causes sickle cell anaemia and the mutant haemoglobin molecule undergoes polymerisation under low oxygen tension causing the change in the shape of RBC from biconcave disc to elongated sickle cell like.
(iii) (a) : Due to mutation X, GAG mutates to GAA. But both GAG and GAA code for glutamic acid and hence there is no change in shape of RBC whereas in mutation Y, GUG is substituted by GAA that codes for valine and so the RBCs become sickle shaped.
(iv) (a) : Mutation Y causes sickle cell anaemia that is controlled by a single pair of allele, HbA and HbS Out of three possible genotypes only homozygous individuals for HbS (HbS HbS) show the diseased phenotype.
(v) (d) : Given pedigree chart for sickle-cell anaemia can be illustrated as :
-
(i) (c) : In humans, free earlobes is dominant over attached earlobes.
(ii) (b)
(iii) (a) : If a female with attached earlobes (ee) married a male with free lobe (EE) and sparse hair on pinna then chance of any progeny to have attached ear lobe is zero. It can be depicted as follows:
(iv) (b) : If a man with attached earlobe (ee) and hairy pinna married a woman with attached earlobes (ee) than 100% chances of sons to have hairy pinna as hypertrichosis or hairy pinna is Y linked feature.
(v) (b) : If a male with attached earlobe sparse hair on pinna married a female with attached earlobe then all daughters have an attached earlobe.
Case Study Questions






































