CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Principles of Inheritance and Variation Case Study Questions With Solution2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Principles of Inheritance and Variation Case Study Questions With Solution2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
Case Study Questions
-
Study the pedigree chart showing the pattern of inheritance of blood group character in a family.
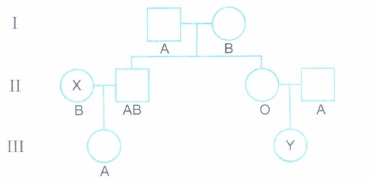
(a) Give the genotypes of the parents in generation I.
(b) State the possible genotypes of the individuals.
(i) X in generation II.
(ii) Y in generation III.
(c) How does the inheritance of this blood group explain codominance?(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below :
During a study of inheritance of two genes, teacher asked students to perform an experiment. The students crossed white eyed, yellow bodied female Drosophila with a red eyed, brown bodied male Drosophila (i.e., wild). They observed that progenies in F2 generation had 1.3 percent recombinants and 98.7 percent parental type combinations. The experimental cross with results is shown in the given figure.[Note: Dominant wild type alleles are represented with (+) sign in superscript.]
(i) By conducting the given experiment, teacher can conclude that
A. Genes for eye colour and body colour are linked
B. Genes for eye colour and body colour show complete linkage
C. Linked gene remain together and are inherited(a) A and B only (b) B only (c) A and C only (d) A, Band C (ii) Teacher asked to conduct an experiment on Drosophila because
(a) the male and female flies are easily distinguishable (b) it completes its life cycle in about two weeks (c) a single mating could produce a large number of progeny flies (d) all of these. (iii) Genes white eyed and yellow bodied located very close to one another on the same chromosome tend to be transmitted together are called
(a) allelomorphs (b) identical genes (c) linked genes (d) recessive genes (iv) Select the correct statement regarding the given experiment.
(a) The physical distance between two genes determines strength of linkage (b) The physical distance between two genes determines frequency of crossing over (c) The two linked genes always segregate independently of each other (d) Both (a) and (b) (v) Assertion : When yellow bodied, white eyed Drosophila females were hybridised with brown-bodied, red eyed males; and FI progeny was intercross ed, F2 ratio deviated from 9: 3: 3: 1.
Reason : When two genes in a dihybrid are on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combinations are much higher than the non-parental type.(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion (c) Assertion is true but reason is false (d) Both assertion and reason are false (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below :
Turner's syndrome is an example of mono somy. It is formed by the union of an allosome free egg and a normal 'X' containing sperm or a normal egg and an allosome free sperm. The individual has 2n = 45 chromosomes (44 + X0) instead of 46. Such individuals are sterile females who have rudimentary ovaries, under developed breasts, small uterus, short stature, webbed neck and abnormal intelligence. They may not menstruate or ovulate. This disorder can be treated by giving female sex hormone to the women from the age of puberty to make them develop breasts and have menstruation. This makes them feel more normal.
(i) Number of Barr body present in a female with Turner's syndrome is(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) < 2. (ii) Turner's syndrome is an example of
(a) aneuploidy (b) euploidy (c) polyploidy (d) autosomal abnormality (iii) Turner's syndrome is a/an
(a) autosomal recessive Mendelian disorder (b) autosomal dominant Mendelian disorder (c) sex linked Mendelian disorder (d) chromosomal disorder (iv) Which of the following statements regarding Turner's syndrome is incorrect?
(a) It is a case of monosomy of chromosomes (b) The suffering individual is a sterile female having one 'X' chromosome missing in the cells (c) The problem is due to an extra chromosome (d) The individual are of short stature (v) Assertion : Turner's syndrome is caused due to absence of anyone of the X and Y sex chromosome.
Reason : Individuals suffering from Turner's syndrome show masculine as well as feminine development(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion (c) Assertion is true but reason is false (d) Both assertion and reason are false (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Haemophilia is a sex linked disease which is also known as bleeder's disease as the patient will continue to bleed even from a minor cut since he or she does not possess the natural phenomenon of blood clotting due to absence of anti-haemophilic globulin or factor VIII and plasma thromboplastin factor IX essential for it. As a result of continuous bleeding the patient may die of blood loss. Colour blindness is another type of sex linked trait in which the eye fails to distinguish red and green colours. Vision is however, not affected and the colour blind can, lead a normal life, reading, writing and driving (distinguishing traffic lights by their position).(i) If a haemophilic man marries a woman whose father was haemophilic and mother was normal then which of the following holds true for their progenies?(a) Of the total number of daughters, 50% daughters are carrier and 50% are haemophilic (b) All the daughters are haemophilic. (c) All sons are haemophilic and all daughters are normal. (d) All sons are normal, all daughters are carriers. (ii) A man whose father was colourblind and mother was normal marries a woman whose father was haemophilic and mother was normal. Which of the following is true for their progenies? [Note: Percentage is from the total number of progenies.
(a) 25% female progenies carry the gene for both haemophilia and colourblindness (b) 25% male progenies carry only the gene of colourblindness (c) 25% female progenies carry only the gene of colourblindness. (d) 25% male progenies and 25% female progenies carry the gene of haemophilia (iii) Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding haemophilia?
(a) It is a dominant disease (b) A single protein involved in clotting of blood is affected (c) It is recessive disease (d) It is Mendelian disorder (iv) Anup is having colourblindness and is married to Soni who is normal. What is the chance that their son will have the disease?
(a) 100% (b) 50% (c) 25% (d) 0% (v) Refer to the given cross
Select the correct option regarding 1, 2, 3 and 4.(a) 1. Colourblind carrier female
2. Colourblind haemophilic female
3. Normal male
4. Haemophilic male(b) 1.Colourblind people
2.Haemophilic female
3.Normal male
4..Haemophilic male(c) 1. Colourblind female
2. Colourblind and haemophilic female
3. Normal male
4. Normal male(d) 1.Colourblind carrier female
2.Normal female
3.Normal male
4.Haemophilic male(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
A relevant portion of \(\beta\)-chain of haemoglobin of a normal human is as follows
The codon for the sixth amino acid is GAG. The sixth codon GAG mutates to GAA as a result of mutation X and into GUG as a result of mutation Y.
(i) Which of the following is incorrect statement?(a) Mutation X carries no change in shape of red blood cells. (b) Mutation Y causes change in shape of red blood cell shape (c) Both mutations X and Y causes change in shape of red blood cell shape. (d) Both (a) and (b) (ii) Due to mutation Y the shape of RBCs under oxygen tension will be
(a) biconcave disc like (b) elongated and curve (c) circular (d) spherical (iii) GUG is code for
(a) valine (b) proline (c) glutamic acid (d) leucine (iv) Which of the following genotype shows diseased phenotype due to mutation Y?
(a) Hbs Hbs (b) HbA Hbs (c) HbA HbA (d) Both (a) and (b) (v) Study the given pedigree chart for sickle-cell anaemia and select the most appropriate option for the genotypes.
Genotypes of parents Genotypes of 1st and 3rd child in F1 (a) HbA HbS, HbA HbA HbA HbA, HbA HbS (b) HbA HbS, HbA HbS HbA HbA, HbA HbA (c) HbA HbA, HbA HbS HbA HbA, HbS HbS (d) HbA Hbs, HbA Hbs HbA HbS, HbS HbS (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Principles of Inheritance and Variation Case Study Questions With Solution2021 Answer Keys
-
(a) Father - IAi, Mother IBi
(b) (i) -IBi
(ii) IAi or ii
(C) (i) The alleles IAand IBofthe blood group character are equally dominant and both of them express themselves when present together, resulting in blood group AB. -
(i) (c) : By conducting the given cross teacher can conclude that the genes for eye colour and body colour are linked. Thus these genes were very tightly linked and showed very low recombination.
(ii) (d)
(iii) (c) : Genes located very close to one another on the same chromosome tend to be transmitted together and are called linked genes.
(iv) (a) : The physical distance between two genes determines both the strength of the linkage and the frequency of the crossing over between two genes. The strength of the linkage increases with the closeness of the two genes. On the other hand the frequency of crossing over increases with the increase in the physical distance between the two genes.
(v) (a) : In Drosophila, the genes for body and eye colour are located on X chromosome. When two genes in a dihybrid cross are situated on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combination are higher than non-parental type. This occurs due to physical association or linkage of the two genes while non-parental gene combinations due to recombination between two genes. Thus, linkage and recombirtation deviates the ratio from Mendelian ratio of a dihybrid cross (9 : 3 : 3 : 1). -
(i) (a) : Barr body is a structure consisting of a condensed X chromosome that is found in nondividing nuclei of female mammals. The presence of Barr body is used to confirm the sex of athletes in sex determination tests. It is named after the Canadian anatomist M.L. Barr, who identified it. The number of Barr bodies is one less than total number of X chromosomes. In Turner's syndrome genotype is 45 + X0,so, the number of Barr body is O.
(ii) (a) : Failure of segregation of chromatids during cell division result in the gain or loss of a chromosomes called aneuploidy. For example, Turner's syndrome results due to loss of X chromosome in human females.
(iii) (d) : Turner's syndrome is a chromosomal disorder that occurs due to absence of one chromosome.
(iv) (c) : In Turner's syndrome individual lacks one X chromosome. This situation is known as monosomy.
(v) (d): Turner's syndrome occurs due to absence of X chromosome. Individuals having a single X chromosome 22A + X0 (45) have female sexual differentiation but ovaries are rudimentary. Other associated phenotypes of this condition are short stature, webbed-neck, broad chest, lack of secondary sexual characteristics and sterility. Thus, any imbalance in the copies of the sex chromosomes may disrupt the genetic information necessary for normal sexual development. -
(i) (a) : When a haemophilic man (Xhy) marries a woman whose father was haemophilic and mother was normal i.e., carrier woman (XXh), then 50% daughters are carriers and 50% are haemophilic. This can be explained as follows:
(ii) (d) : When a man whose father was colourblind and mother was normal (i.e., normal man XY) marries a woman whose father was haemophilic and mother was normal (i.e., carrier haemophilic woman XhX), then 25% male progenies and 25% female progenies carry the gene of haemophilia.
(iii) (a) : Haemophilia is sex linked recessive Mendelian disorder.
(iv) (d) : When Anup who is colourblind (Xcy) marries Soni who is normal (XX) then 0%, chances that their son will have colourblindness.
(v) (a) -
(i) (C) : Due to mutation X, GAG mutates to GAA. But both GAG and GAA code for glutamic acid and hence there is no change in shape of RBC whereas in mutation Y, GUG is substituted by GAA that codes for valine and so the RBCs become sickle shaped.
(ii) (b) : Mutation Y causes sickle cell anaemia and the mutant haemoglobin molecule undergoes polymerisation under low oxygen tension causing the change in the shape of RBC from biconcave disc to elongated sickle cell like.
(iii) (a) : Due to mutation X, GAG mutates to GAA. But both GAG and GAA code for glutamic acid and hence there is no change in shape of RBC whereas in mutation Y, GUG is substituted by GAA that codes for valine and so the RBCs become sickle shaped.
(iv) (a) : Mutation Y causes sickle cell anaemia that is controlled by a single pair of allele, HbA and HbS Out of three possible genotypes only homozygous individuals for HbS (HbS HbS) show the diseased phenotype.
(v) (d) : Given pedigree chart for sickle-cell anaemia can be illustrated as :






































