CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Case Study Questions 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
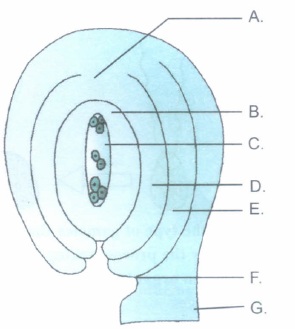
The diagram of an anatropous ovule is presented above.
(a) Give the technical term for ovule.
(b) Identify and name the part that
(i) attaches the ovule to the placenta
(ii) remains as perisperm in some seeds.
(iii) forms the testa of seed.
(iv) represents the basal part of the ovule.
(v) represents the female gametophyte.(a) -
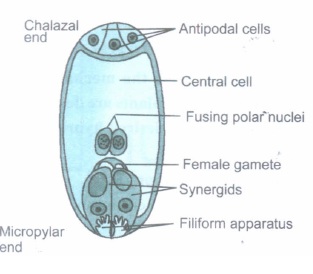
A fully developed embryo sac
A fully-developed and mature embryo sac is shown above.
(a) Name the cell from which it has developed.
(b) What is the ploidy level of its nuclei?
(c) What is filiform apparatus? Mention its significance.(a) -
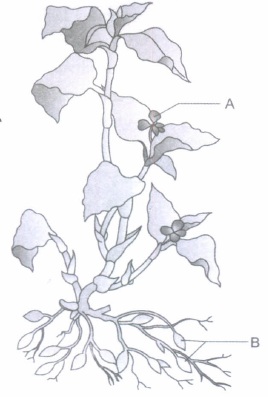
Identify the types of flowers A and B on the Commelina plant shown above.
(b) Mention the type(s) of pollination that can occur in each of them.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Apomixis is a mode of reproduction which does not involve formation of zygote through gametic fusion. In plants, apomixis commonly mimics sexual reproduction but produces seeds without fertilisation. There are several methods of apomictic development in seeds. The two common ones are recurrent agamospermy and adventive embryony.
(i) Apomixis is a type of reproduction in plants in which
(a) fertilisation does not take place
(b) male nucleus takes part in fertilisation
(c) pollen fusion takes place
(d) generative nucleus takes part in fertilisation(ii) Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding recurrent agamospermy?
(a) It is the formation of seed that has an embryo formed without meiosis and syngamy
(b) All the cells of embryo sac are diploid.
(c) An embryo develops directly from a diploid cell other than egg like that of nucleus and integument
(d) None of these
(iii) Adventive embryony is found in(a) Citrus (b) Opuntia (c) Apple (d) Both (a) and (b). (iv) Formation of embryo directly from diploid egg without fertilisation is called
(a) apospory (b) diplospory (c) polyembryony (d) diploid parthenogenesis (v) If any somatic cell of sporophyte produces gametophyte without reduction division, it is called
(a) parthenogenesis (b) apogamy (c) apospory (d) amphimixis (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (v) to (v) given below:
A typical angiospermic ovule is a small structure attached to the placenta by means of a stalk called funicle. The body of the ovule fuses with funicle in the region called hilum. Each ovule has one or two protective envelopes called integuments. Integuments encircle the nucellus except at the tip where a small opening called the micropyle is formed. Mature ovules are classified on the basis of funiculus. It can be orthotropous, anatropous, hemitropous, campylotropous, etc.
(i) The body of the ovule consists of a mass of parenchymatous cells called(a) integuments (b) nucellus (c) hilum (d) funiculus (ii) Refer to the given figure and select the correct statement regarding it.
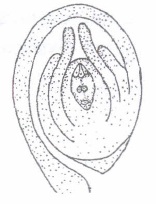
(a) This type of ovule is found in cactus.
(b) The micropyle comes to lie close to the funiculus due to unilateral growth of ovule.
(c) It is most common type of ovule found in the members of Chenopodiaceae
(d) It is half inverted ovule.(iii) Identify the parts labelled as A, B, Cand D in the given figure and select the correct option
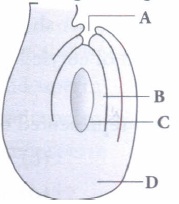
A B C D (a) Chalaza Female gametophyte Embryo sac Micropyle (b) Chalaza Nucellus Embryo sac Micropyle (c) Micropyle Egg Embryo sac Chalaza (d) Micropyle Nucellus Embryo sac Chalaza (iv) Mature ovules are classified on the basis of funiculus. If micropyle lie close to the funiculus, the ovule is termed as
(a) orthotropous (b) anatropous (c) hemitropous (d) campylotropous (v) In Asphodelus, ovule is
(a) unitegmic (b) tritegmic (c) bitegmic (d) ategmic (a)
Case Study Questions
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
(a) Megasporangium
(b) (i) G. Funicle
(ii) B. Nucellus
(iii) E. Outer integument
(iv) A. Chalaza
(v) C. Embryo sac. -
(a) Megaspore
(b) Haploid
(c) (i) Filiform apparatus refers to the special cellular thickenings in the synergids, towards micropylar tip.
(ii) They play an important role in guiding the pollen tube to enter one of the synergids. -
(a) A - Chasmogamous flower
B - Cleistogamous flower
(b) A - Autogamy, geitonogamy and xenogamy
B - Autogamy only. -
(i) (a)
(ii) (c) : In recurrent agamospermy all the cells of embryo sac are diploid as it is formed directly either from a nuclear cell or diploid megaspore mother cell.
(iii) (d) : In adventive embryony, an embryo develops directly from a diploid cell other than egg like that of nucleus and integument, e.g., Citrus, Opuntia.
(iv) (d) : Formation of embryo directly from diploid egg without fertilisation is called diploid parthenogenesis. It is found in Rubus, apple, Poa.
(v) (c) -
(i) (b)
(ii) (a) : The given figure is of circinotropous ovule where funiculus coiled around the ovule. It is found in the Family Cactaceae.
(iii) (d) : Given figure represents an anatropous ovule where· A, B, C and D represent micropyle, nucellus, embryo sac and chalaza respectively.
(iv) (b) : Depending upon the configuration and orientation of the body of ovule in relation to funiculus, there are six types of ovule - orthotropous (atropous, erect), anatropous (inverted), hemitropous (half inverted), campylotropous (body curved), amphitropous (both body and embryo sac curved) and circinotropous (funiculus coiled around the ovule). Anatropous or inverted ovule is the most common type of ovule found in angiosperms (in 80% of angiosperm families). Here, body of the ovule gets inverted and micropyle is on lower side. Further micropyle and funiculus lie side by side and micropyle is close to hilum.
(v) (b)
Case Study Questions






































