Class 11th Physics - Motion in a Straight Line Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 08 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Physics Subject - Motion in a Straight Line, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Motion in a Straight Line Case Study Questions With Answer Key
11th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Physics
-
It must be clearly understood that distance is not the same as displacement. Distance is a scalar quantity and is given by the total length of the path travelled by the body in a certain interval of time. Displacement is a vector quantity and is given by the shortest distance (in a specified direction) between the initial and the final positions of the body. The direction of the displacement vector is from the initial position to the final position of the motion. Speed IS a scalar quantity. The average speed and average velocity are different in many respect. The direction of the velocity vector is the same as that of the displacement vector. Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity and it is a vector quantity.
(i) Mention a condition when displacement and distance are both equal.
(ii) Define average speed and average velocity.
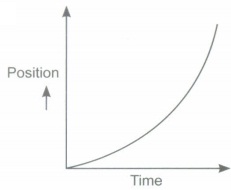
(iii) Draw position-time graph of uniform accelerated motion.
(iv) What does the area under velocity-time graph and time axis signifies?
(v) What does the slope of position-time graph and velocity-time graph represent at any instant?
(vi) Mention a condition when body is at rest but still it has acceleration.
(vii) A body is moving in circular parth with uniform speed. What is the acceleration and average velocity during one complete revolution?(a) -
A sports car passing a police checkpost at 60 km h-1 immediately started slowing down uniformly until its speed was 40 km h-1. It continued to move at the same speed until it was passed by a Police car 1 km from the check post. This police car had started from rest at the check post at the same instant as the sport car had passed the check post. The police car had moved with a constant acceleration until it had passed sports car. Assuming that the time taken by the sports car in slowing down from 60 km h-' to 40 km h-' was equal to the time that it travelled at constant speed before passed by the Police car.
(i) Determine the average velocity of sports car.
(ii) Determine the speed of the police car at the instant when it passed the sports car.
(iii) Determine the acceleration of the police car.
(iv) Draw the velocity-time graph for police car and sport car.
(v) How much time taken by police car to pass the sports car?(a) -
Kinematics is the branch of mechanics which deals with the study of motion of material objects without taking into account the factors affecting the motion. Rest and motion are relative concept and nothing is absolute. The Position of the object at a given instant of time is described in terms of position coordinates. The coordinate system along with a clock constitutes a frame of reference. Frame of reference can be of two types viz: inertial frame of reference and non-inertial frame of reference. When position of body change in a frame of reference, it is said to be in motion which is categorised as uniform and non-uniform. Motion of a body is studied in terms of position-time graph and velocity-time graph.
(i) "Rest and motion are relative not absolute." Comment.
(ii) What are different types of frames of reference? Explain.
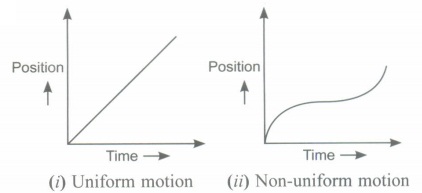
(iii) Draw position-time graph for uniform and Non-uniform motion.
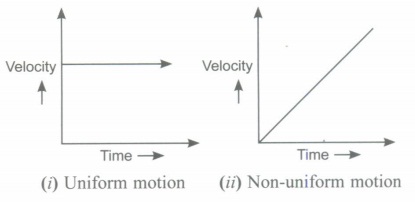
(iv) Draw velocity-time graph for uniform and non-uniform motion.
(v) Relative veolcity of two bodies is zero. What is nature of Position-time graph for it?(a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Motion in a Straight Line Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(i) When a body is moving in straight line in a specific direction then both displacement and distance would be equal in magnitude.
(ii) Average speed is the average distance travelled per unit time
\(\text { or } v=\frac{\text { total distance travelled }}{\text { total time taken }}\)
Average velocity is the average displacement covered per unit time. It is a vector quantity.
\(\bar{v}=\frac{\text { net displacement }}{\text { time taken }}\)
(iii)
(iv) Area under velocity-time graph and time axis is the measure of displacement in that particular interval of time.
(v) Slope of Position-time at any instant represent instantaneous velocity while that of velocity-time represent instantaneous acceleration.
(vi) A body thrown upward then at highest point body comes to rest momentarily but still acceleration is acrting downward.
(vii) During one complete revolution average displacement and velocity is zero while acceleration is acting radially toward the center of circular path. -
(i) Average velocity of sports car for motion
\(v_{a v}=\frac{60+40}{2}=50 \mathrm{~km} \mathrm{~h}^{-1}\)
(ii) Distance = average velocity x time taken
\(1 \mathrm{~km}=\frac{v}{2} \times \frac{2}{90} \Rightarrow v=90 \mathrm{~km} \mathrm{~h}^{-1}\)
(iii) \(v=u+\text { at } \Rightarrow 90=0+a \times \frac{1}{45}\)
or a = 45 x 90 km h-2 = 4050 km h-2
(iv)
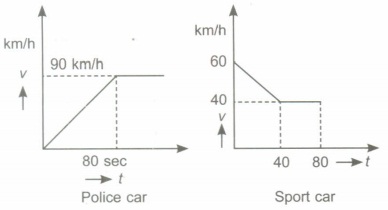
(v) Time taken to cover distance of 1 km by sports car is 2t. 50 x t + 40t = 1 km
\(t =\frac{1}{90} \text { hour }\)
\(2 t =\frac{1}{45} h=\frac{1}{45} \times 60 \times 60=80 \mathrm{sec}\) -
(i) Position of an object is determined with respect to some reference point. When position change with respect to the reference point this indicates motion while when position do not change with respect to the reference point, then it state of rest. So rest and motion are the relative terms because they depend on the observer's frame of reference.
(ii) There are two types of frames of reference.
(i) Inertial frame of reference is one in which Newton's first law of motion holds true.
(ii) Non-inertial frame of reference is one in which Newton's first law of motion does not hold true.
(iii)
(iv)
(v) Position time graph of two bodies for zero relative velocity is Parallel straight line.
Case Study



































