- State Board
-
12th Standard
-

Biology
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Science
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Commerce
-

Economics
-

Maths
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Computer Technology
-

History
-

Accountancy
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Biology
-

Computer Science
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Economics
-

Commerce
-

Accountancy
-

History
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Technology
-

English
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
11th Standard
-

Maths
-

Biology
-

உயிரியல் - தாவரவியல்
-

Economics
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

History
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Computer Science
-

Accountancy
-

Commerce
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Technology
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Commerce
-

Economics
-

Biology
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Accountancy
-

Computer Science
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

Computer Applications
-

History
-

Computer Technology
-

Tamil
-

English
11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
9th Standard
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
6th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
6th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
10th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

English
-

English
10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
7th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
8th Standard
-

கணிதம் - old
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

கணிதம்
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
12th Standard
- CBSE Board
-
12th Standard CBSE
-

Biology
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Maths
-

Accountancy
-

Business Studies
-

Economics
-

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics
-

Computer Science
-

Geography
-

English
-

History
-

Indian Society
-

Physical Education
-

Sociology
-

Political Science
-

Engineering Graphics
-

Bio Technology
-

Entrepreneurship
-

Hindi Elective
-

Home Science
-

Legal Studies
-

Psychology
-

Hindi Core
-

Tamil
12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
11th Standard CBSE
-

Physics
-

Mathematics
-

Chemistry
-

Biology
-

Economics
-

Business Studies
-

Accountancy
-

Computer Science
-

English
-

Geography
-

History
-

Physical Education
-

Psychology
-

Sociology
-

Bio Technology
-

Enterprenership
-

Hindi
-

Home Science
-

Political Science
-

Applied Mathematics
11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
- 10th Standard CBSE
-
9th Standard CBSE
-

Social Science
-

Mathematics
-

Science
-

English
-

Hindi
9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
8th Standard CBSE
-

Social Science
-

Science
-

Mathematics
-

English
8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
7th Standard CBSE
-

Social Science
-

Science
-

Mathematics
-

English
7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
6th Standard CBSE
-

Social Science
-

Science
-

Mathematics
-

English
6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
12th Standard CBSE
- Free Online Test
- News
- Study Materials
-
Students
-

Stateboard Tamil Nadu
-

CBSE Board
-

Free Online Tests
-

Educational News
-

Scholarships
-

Entrance Exams India
-

Video Materials
Study Materials , News and Scholarships
-
-
Students

12th Standard Business Maths English Medium Important 5 Mark Book Back Questions (New Syllabus 2020) Question Bank Software Sep-30 , 2020
12th Standard Business Maths English Medium Important 5 Mark Book Back Questions (New Syllabus 2020)
Important 5 Mark Book Back Questions (New Syllabus 2020)
12th Standard
-
Reg.No. :
Business Maths
Time :
01:00:00 Hrs
Total Marks :
280
-
Show that the equations x + y + z = 6, x + 2y + 3z = 14, x + 4y + 7z = 30 are consistent and solve them.
-
Investigate for what values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ the following system of equations x + y + z = 6,x + 2y + 3z = 10, x + 2y + az = b have
(i) no solution
(ii) a unique solution
(iii) an infinite number of solutions. -
The price of three commodities X, Y and Z are x, y and z respectively Mr. Anand purchases 6 units of Z and sells 2 units of X and 3 units of Y. Mr. Amar purchases a unit of Y and sells 3 units of X and 2units of Z. Mr. Amit purchases a unit of X and sells 3 units of Y and a unit of Z. In the process they earn Rs. 5,000/-, Rs. 2,000/- and Rs. 5,500/- respectively. Find the prices per unit of three commodities by rank method.
-
An automobile company uses three types of Steel S1, S2 and S3 for providing three different types of Cars C1, C2 and C3. Steel requirement R (in tonnes) for each type of car and total available steel of all the three types are summarized in the following table.
Types of Steel Types of Car Total Steel available C1 C2 C3 S1 3 2 4 28 S2 1 1 2 13 S3 2 2 2 14 Determine the number of Cars of each type which can be produced by Cramer’s rule.
-
Two types of soaps A and B are in the market. Their present market shares are 15% for A and 85% for B. Of those who bought A the previous year, 65% continue to buy it again while 35% switch over to B. Of those who bought B the previous year, 55% buy it again and 45% switch over to A. Find their market shares after one year and when is the equilibrium reached?
-
Solve the equations x + 2y + z = 7, 2x − y + 2z = 4, x + y − 2z = −1 by using Cramer’s rule
-
Solve the following equation by using Cramer’s rule
x + 4y + 3z = 2, 2x−6y + 6z = −3, 5x− 2y + 3z = −5 -
Integrate the following with respect to x.
\(\frac { { 4x }^{ 2 }+2x+6 }{ { \left( x+1 \right) }^{ 2 }\left( x-3 \right) } \) -
Integrate the following with respect to x.
ex (1+ x) log(xex) -
Evaluate \(\int _{ -1 }^{ 1 }{ { ({ x }^{ 3 }+{ 3x }^{ 2 }) }^{ 3 } } \) (x2 + 2x)dx
-
Evaluate \(\int _{ 0 }^{ \frac { \pi }{ 2 } }\) x sin x dx
-
Evaluate \(\int _{ 2 }^{ 5 }{ \frac { \sqrt { x } }{ \sqrt { x } +\sqrt { 7-x } } } \) dx
-
Evaluate the following integrals as the limit of the sum:
\(\int _{ 0 }^{ 1 }{ (x+4) } \)dx -
Evaluate the following integrals:
\(\int _{ 0 }^{ 3 }{ \frac { xdx }{ \sqrt { x+1 } +\sqrt { 5x+1 } } } \) -
Calculate the area bounded by the parabola y2 = 4ax and its latus rectum.
-
The marginal cost C'(x) and marginal revenue R'(x) are given by C'(x) = 50 + \(\frac{x}{50}\) and R'(x) = 60. The fixed cost is Rs. 200. Determine the maximum profit
-
When the Elasticity function is \(\frac { x }{ x-2 } \). Find the function when x = 6 and y = 16.
-
The marginal cost of production of a firm is given by C'(x) = 5 + 0.13x, the marginal revenue is given by R'(x) = 18 and the fixed cost is Rs. 120. Find the profit function.
-
The demand equation for a product is pd = 20 − 5x and the supply equation is ps = 4x + 8. Determine the consumer’s surplus and producer’s surplus under market equilibrium.
-
Solve : x - y \(\frac { dx }{ dy } =a\left( { x }^{ 2 }+\frac { dx }{ dy } \right) \)
-
If the marginal cost of producing x shoes is given by (3xy + y2)dx + (x2 + xy)dy = 0 and the total cost of producing a pair of shoes is given by Rs. 12. Then find the total cost function.
-
Solve the following homogeneous differential equations.
\(x\frac { dy }{ dx } -y=\sqrt { { x }^{ 2 }+{ y }^{ 2 } } \) -
Solve (x2 + 1)\(\frac { dy }{ dx } \) + 2xy = 4x2
-
Solve the following:
\(\frac{d y}{d x}+\frac{3 x^{2}}{1+x^{3}} y=\frac{1+x^{2}}{1+x^{3}}\) -
(D2 − 3D + 2)y = e3x which shall vanish for x = 0 and for x = log 2
-
Solve the following differential equations (3D2 + D − 14)y = 13e2x
-
Solve (x2 + y2)dx + 2xy dy = 0
-
Using Newton’s formula for interpolation estimate the population for the year 1905 from the table:
Year 1891 1901 1911 1921 1931 Population 98.752 1,32,285 1,68,076 1,95,690 2,46,050 -
The following data are taken from the steam table
Temperature C0 140 150 160 170 180 Pressure kg f / cm2 3.685 4.854 6.302 8.076 10.225 Find the pressure at temperature t = 1750
-
Using interpolation estimate the output of a factory in 1986 from the following data
Year 1974 1978 1982 1990 Output in 1000 tones 25 60 80 170 -
Using Lagrange’s interpolation formula find a polynomial which passes through the points (0, –12), (1, 0), (3, 6) and (4,12).
-
The distribution of a continuous random variable X in range (–3, 3) is given by p.d.f.
\(f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{l} \frac{1}{16}(3+x)^{2},-3 \leq x \leq-1 \\ \frac{1}{16}\left(6-2 x^{2}\right),-1 \leq x \leq 1 \\ \frac{1}{16}(3-x)^{2}, 1 \leq x \leq 3 \end{array}\right.\)
Verify that the area under the curve is unity. -
Determine the mean and variance of the random variable X having the following probability distribution.
X=x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 P(x) 0.15 0.10 0.10 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.05 0.02 0.28 0.20 -
The probability density function of a continuous random variable X is
\(f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{l} a+b x^{2}, 0 \leq x \leq 1 \\ 0, \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right.\)
where a and b are some constants. Find
(i) a and b if E(X)\(\frac{3}{5}\)
(ii) Var(X). -
If the average rain falls on 9 days in every thirty days, find the probability that rain will fall on atleast two days of a given week.
-
If X is a normal variate with mean 30 and SD 5. Find the probabilities that
(i) 26 ≤ X ≤ 40
(ii) X > 45 -
A bank manager has observed that the length of time the customers have to wait for being attended by the teller is normally distributed with mean time of 5 minutes and standard deviation of 0.6 minutes. Find the probability that a customer has to wait
(i) for less than 6 minutes
(ii) between 3.5 and 6.5 minutes -
Out of 750 families with 4 children each, how many families would be expected to have
(i) atleast one boy
(ii) atmost 2 girls
(iii) and children of both sexes? Assume equal probabilities for boys and girls. -
A car hiring firm has two cars. The demand for cars on each day is distributed as a Poisson variate, with mean 1.5. Calculate the proportion of days on which
(i) Neither car is used
(ii) Some demand is refused -
In a distribution 30% of the items are under 50 and 10% are over 86. Find the mean and standard deviation of the distribution.
-
Time taken by a construction company to construct a flyover is a normal variate with mean 400 labour days and standard deviation of 100 labour days. If the company promises to construct the flyover in 450 days or less and agree to pay a penalty of Rs. 10,000 for each labour day spent in excess of 450. What is the probability that
(i) the company pays a penalty of atleast Rs. 2,00,000?
(ii) the company takes at most 500 days to complete the flyover? -
Using the following random number table,
Tippet’s random number table 2952 6641 3992 9792 7969 5911 3170 5624 4167 9524 1545 1396 7203 5356 1300 2693 2670 7483 3408 2762 3563 1089 6913 7991 0560 5246 1112 6107 6008 8125 4233 8776 2754 9143 1405 9025 7002 6111 8816 6446 Draw a sample of 10 children with their height from the population of 8,585 children as classified here under.
Height (cm) 105 107 109 111 113 115 117 119 121 123 125 Number of children 2 4 14 41 83 169 394 669 990 1223 1329 Height(cm) 127 129 131 133 135 137 139 141 143 145 No. of children 1230 1063 646 392 202 79 32 16 5 2 -
An auto company decided to introduce a new six cylinder car whose mean petrol consumption is claimed to be lower than that of the existing auto engine. It was found that the mean petrol consumption for the 50 cars was 10 km per litre with a standard deviation of 3.5 km per litre. Test at 5% level of significance, whether the claim of the new car petrol consumption is 9.5 km per litre on the average is acceptable.
-
Explain in detail about simple random sampling with a suitable example.
-
A sample of 100 students are drawn from a school. The mean weight and variance of the sample are 67.45 kg and 9 kg. respectively. Find
(a) 95% and
(b) 99% confidence intervals for estimating the mean weight of the students. -
Calculate the seasonal index for the monthly sales of a product using the method of simple averages.
Months Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 2001 15 41 25 31 29 47 41 19 35 38 40 30 2002 20 21 27 19 17 25 29 31 35 39 30 44 2003 18 16 20 28 24 25 30 34 30 38 37 39 -
Construct Fisher’s price index number and prove that it satisfies both Time Reversal Test and Factor Reversal Test for data following data.
Commodities Base Year Current Year Price Quantity Price Quantity Rice 40 5 48 4 Wheat 45 2 42 3 Rent 90 4 95 6 Fuel 85 3 80 2 Transport 50 5 65 8 Miscellaneous 65 1 72 3 -
Construct the cost of living index number for 2011 on the basis of 2007 from the given data using family budget method.
Commodities Price Weights 2007 2011 A 350 400 40 B 175 250 35 C 100 115 15 D 75 105 20 E 60 80 25 -
The sales of a commodity in tones varied from January 2010 to December 2010 as follows:
In year 2010 Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Sales (in tones) 280 240 270 300 280 290 210 200 230 200 230 210 Fit a trend line by the method of semi-average.
-
Calculate price index number for 2005 by
(a) Laspeyre’s
(b) Paasche’s methodCommodity 1995 2005 Price Quantity Price Quantity A 5 60 15 70 B 4 20 8 35 C 3 15 6 20 -
Construct the cost of living Index number for 2015 on the basis of 2012 from the following data using family budget method.
Commodity Price Weight 2012 2015 Rice 250 280 10 Wheat 70 280 5 Corn 150 170 6 Oil 25 35 4 Dhal 85 90 3 -
Construc \(\overset {-}{X}\) and R charts for the following data:
Sample Number Observations 1 32 36 42 2 28 32 40 3 39 52 28 4 50 42 31 5 42 45 34 6 50 29 21 7 44 52 35 8 22 35 44 ( Given for n = 3, A2 = 0.58,D3 = 0 and D4 = 2.115)
-
Fit a straight line trend by the method of least squares to the following data.
Year 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 Sales 50.3 52.7 49.3 57.3 56.8 60.7 62.1 58.7 -
The following data gives the average life(in hours) and range of 12 samples of 5 lamps each. The data are
Sample No 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sample Mean 1080 1390 1460 1380 1230 1370 Sample Range 410 670 180 320 690 450 Sample No 7 8 9 10 11 12 Sample Mean 1310 1630 1580 1510 1270 1200 Sample Range 380 350 270 660 440 310 Construct control charts for mean and range. Comment on the control limits.
-
A departmental head has four subordinates and four tasks to be performed. The subordinates differ in efficiency and the tasks differ in their intrinsic difficulty. His estimates of the time each man would take to perform each task is given below :
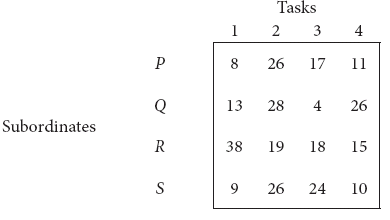
How should the tasks be allocated to subordinates so as to minimize the total man-hours?
Part A
56 x 5 = 280
*****************************************
12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Videos
TN 12th Business Maths Applications of Matrices and Determinants 50 Important 1 Marks Questions With
TN Class 12th 2024 Business Maths and Statistics Applications of Matrices and Determinants Study Materials TN State Board / Matriculation 12th Business Maths and Statistics Subject - Applications of Matrices and Determinants One Mark Question and Answers






 12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Syllabus
12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Syllabus  12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Study Materials
12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Study Materials 12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics MCQ Practise Tests
12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics MCQ Practise Tests 

Reviews & Comments about 12th Standard Business Maths English Medium Important 5 Mark Book Back Questions (New Syllabus 2020)
Write your Comment