- State Board
-
12th Standard
-

Biology
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Science
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Commerce
-

Economics
-

Maths
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Computer Technology
-

History
-

Accountancy
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Biology
-

Computer Science
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Economics
-

Commerce
-

Accountancy
-

History
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Technology
-

English
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
11th Standard
-

Maths
-

Biology
-

உயிரியல் - தாவரவியல்
-

Economics
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

History
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Computer Science
-

Accountancy
-

Commerce
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Technology
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Commerce
-

Economics
-

Biology
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Accountancy
-

Computer Science
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

Computer Applications
-

History
-

Computer Technology
-

Tamil
-

English
11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
9th Standard
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
6th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
6th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
10th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

English
-

English
10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
7th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
8th Standard
-

கணிதம் - old
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

கணிதம்
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
12th Standard
- CBSE Board
-
12th Standard CBSE
-

Biology
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Maths
-

Accountancy
-

Business Studies
-

Economics
-

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics
-

Computer Science
-

Geography
-

English
-

History
-

Indian Society
-

Physical Education
-

Sociology
-

Political Science
-

Engineering Graphics
-

Bio Technology
-

Entrepreneurship
-

Hindi Elective
-

Home Science
-

Legal Studies
-

Psychology
-

Hindi Core
-

Tamil
12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
11th Standard CBSE
-

Physics
-

Mathematics
-

Chemistry
-

Biology
-

Economics
-

Business Studies
-

Accountancy
-

Computer Science
-

English
-

Geography
-

History
-

Physical Education
-

Psychology
-

Sociology
-

Bio Technology
-

Enterprenership
-

Hindi
-

Home Science
-

Political Science
-

Applied Mathematics
11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
- 10th Standard CBSE
-
9th Standard CBSE
-

Social Science
-

Mathematics
-

Science
-

English
-

Hindi
9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
8th Standard CBSE
-

Social Science
-

Science
-

Mathematics
-

English
8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
7th Standard CBSE
-

Social Science
-

Science
-

Mathematics
-

English
7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
6th Standard CBSE
-

Social Science
-

Science
-

Mathematics
-

English
6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
12th Standard CBSE
- Free Online Test
- News
- Study Materials
-
Students
-

Stateboard Tamil Nadu
-

CBSE Board
-

Free Online Tests
-

Educational News
-

Scholarships
-

Entrance Exams India
-

Video Materials
Study Materials , News and Scholarships
-
-
Students

12th Standard Business Maths English Medium Sample 5 Mark Book Back Questions (New Syllabus 2020) Question Bank Software Sep-30 , 2020
12th Standard Business Maths English Medium Sample 5 Mark Book Back Questions (New Syllabus 2020)
Sample 5 Mark Book Back Questions (New Syllabus 2020)
12th Standard
-
Reg.No. :
Business Maths
Time :
01:00:00 Hrs
Total Marks :
240
-
Find k, if the equations x + y + z = 7, x + 2y + 3z = 18, y + kz = 6 are inconsistent
-
Show that the following system of equations have unique solution:
x + y + z = 3, x + 2y + 3z = 4, x + 4y + 9z = 6 by rank method. -
The price of 3 Business Mathematics books, 2 Accountancy books and one Commerce book is Rs. 840. The price of 2 Business Mathematics books, one Accountancy book and one Commerce book is Rs. 570. The price of one Business Mathematics book, one Accountancy book and 2 Commerce books is Rs. 630. Find the cost of each book by using Cramer’s rule.
-
The subscription department of a magazine sends out a letter to a large mailing list inviting subscriptions for the magazine. Some of the people receiving this letter already subscribe to the magazine while others do not. From this mailing list, 45% of those who already subscribe will subscribe again while 30% of those who do not now subscribe will subscribe. On the last letter, it was found that 40% of those receiving it ordered a subscription. What percent of those receiving the current letter can be expected to order a subscription?
-
Find k if the equations x + y + z = 1, 3x − y − z = 4, x+ 5y + 5z = k are inconsistent.
-
Solve the following equation by using Cramer’s rule
2x + y −z = 3, x + y + z =1, x− 2y− 3z = 4 -
Integrate the following with respect x
\(\frac { 3x+2 }{ \left( x-2 \right) \left( x-3 \right) } \) -
Evaluate \(\int\left[\frac{1}{\log x}-\frac{1}{(\log x)^{2}}\right] d x\)
-
Evaluate \(\int _{ 2 }^{ 3 }{ \frac { { x }^{ 4 }+1 }{ { x }^{ 2 } } } dx\)
-
Evaluate \(\int _{ 1 }^{ 2 }{ \frac { 1 }{ (x+1)(x+2) } } dx\)
-
Evaluate \(\int _{ 0 }^{ \frac { \pi }{ 2 } }{ \frac { \sin x }{ \sin x+\cos x } } \) dx
-
Evaluate the integral as the limit of a sum: \(\int _{ 1 }^{ 2 }{ (2x+1) } dx\)
-
Evaluate the following integrals as the limit of the sum:
\(\int _{ 0 }^{ 1 }{ { x }^{ 2 } } dx\) -
Using integration find the area of the circle whose center is at the origin and the radius is a units.
-
A firm has the marginal revenue function given by MR = \(\frac { a }{ { (x+b) }^{ 2 } } \) - c where x is the output and a, b, c are constants. Show that the demand function is given by \(x=\frac { a }{ b(p+c) } -b\).
-
Elasticity of a function \(\frac{Ey}{Ex}\) is given by \(\frac{Ey}{Ex}\) = \(\frac { -7x }{ (1-2x)(2+3x) } \). Find the function when x = 2, y = \(\frac{3}{8}\)
-
A firm’s marginal revenue function is MR = 20e-x/10 \(\left( 1-\frac { x }{ 10 } \right) \). Find the corresponding demand function.
-
Find the consumer’s surplus and producer’s surplus for the demand function pd = 25 − 3x and supply function ps = 5 + 2x.
-
Solve 3extan ydx +(1 + ex)sec2ydy = 0 given y(0) = \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \)
-
Solve the differential equation \(\frac { dy }{ dx } =\frac { x-y }{ x+y } \)
-
Solve the following homogeneous differential equations.
\((x-y)\frac { dy }{ dx } =x+3y\). -
Solve the following:
\(\frac { dy }{ dx } \)+ ytan x = cos3 x -
Suppose that \({ Q }_{ d }=30-5P+2\frac { dp }{ dt } +\frac { { d }^{ 2 }P }{ { dt }^{ 2 } } \) and Qs = 6 + 3P. Find the equilibrium price for market clearance.
-
Evaluate \(\Delta \)\(\left[ \frac { 5x+12 }{ { x }^{ 2 }+5x+6 } \right] \) by taking ‘1’ as the interval of differencing.
-
Using Lagrange’s interpolation formula find y(10) from the following table:
x 5 6 9 11 y 12 13 14 16 -
Using interpolation estimate the output of a factory in 1986 from the following data
Year 1974 1978 1982 1990 Output in 1000 tones 25 60 80 170 -
Find f(0.5) if f(−1) = 202, f (0)= 175, f(1) = 82 and f(2) = 55
-
The amount of bread (in hundreds of pounds) x that a certain bakery is able to sell in a day is found to be a numerical valued random phenomenon, with a probability function specified by the probability density function f(x) is given by
\(f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{l} Ax,for \ 0≤x10 \\ A(20−x),for \ 10 ≤x< 20 \\ 0,\quad \quad \quad otherwise \end{array}\right.\)
(a) Find the value of A.
(b) What is the probability that the number of pounds of bread that will be sold tomorrow is
(i) More than 10 pounds,
(ii) Less than 10 pounds, and
(iii) Between 5 and 15 pounds? -
Suppose that the time in minutes that a person has to wait at a certain station for a train is found to be a random phenomenon with a probability function specified by the distribution function\(F(x)\begin{cases} 0,\quad \text{for}\quad x<0 \\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } ,\quad \text{for}\quad 0\le x<1 \\ 0,\quad \text{for}\quad 1\le x<2\quad \\ \frac { 1 }{ 4 } ,\quad \text{for}\quad 2\le x<4 \\ 0,\quad \text{for}\quad x\ge 4 \end{cases}\)
(a) Is the distribution function continuous? If so, give its probability density function?
(b) What is the probability that a person will have to wait
(i) more than 3 minutes,
(ii) less than 3 minutes and
(iii) between 1 and 3 minutes? -
The probability density function of a continuous random variable X is
\(f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{l} a+b x^{2}, 0 \leq x \leq 1 \\ 0, \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right.\)
where a and b are some constants. Find
(i) a and b if E(X)\(\frac{3}{5}\)
(ii) Var(X). -
What is the probability that a standard normal variate Z will be
(i) greater than 1.09
(ii) less than -1.65
(iii) lying between -1.00 and 1.96
(iv) lying between 1.25 and 2.75 -
900 light bulbs with a mean life of 125 days are installed in a new factory. Their length of life is normally distributed with a standard deviation of 18 days. What is the expected number of bulbs expire in less than 95 days?
-
An experiment succeeds twice as often as it fails, what is the probability that in next five trials there will be
(i) three successes and
(ii) at least three successes -
Time taken by a construction company to construct a flyover is a normal variate with mean 400 labour days and standard deviation of 100 labour days. If the company promises to construct the flyover in 450 days or less and agree to pay a penalty of Rs. 10,000 for each labour day spent in excess of 450. What is the probability that
(i) the company pays a penalty of atleast Rs. 2,00,000?
(ii) the company takes at most 500 days to complete the flyover? -
A sample of 100 measurements at breaking strength of cotton thread gave a mean of 7.4 and a standard deviation of 1.2 gms. Find 95% confidence limits for the mean breaking strength of cotton thread.
-
The mean breaking strength of cables supplied by a manufacturer is 1,800 with a standard deviation 100. By a new technique in the manufacturing process it is claimed that the breaking strength of the cables has increased. In order to test this claim a sample of 50 cables is tested. It is found that the mean breaking strength is 1,850. Can you support the claim at 0.01 level of significance.
-
Calculate the seasonal index for the monthly sales of a product using the method of simple averages.
Months Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year 2001 15 41 25 31 29 47 41 19 35 38 40 30 2002 20 21 27 19 17 25 29 31 35 39 30 44 2003 18 16 20 28 24 25 30 34 30 38 37 39 -
Calculate Fisher’s price index number and show that it satisfies both Time Reversal Test and Factor Reversal Test for data given below.
Commodities Base Year Current Year Price Quantity Price Quantity Rice 10 5 11 6 Wheat 12 6 13 4 Rent 14 8 15 7 Fuel 16 9 17 8 Transport 18 7 19 5 Miscellaneous 20 4 21 3 -
Calculate the cost of living index number by consumer price index number for the year 2016 with respect to base year 2011 of the following data
\(\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|} \hline & {\text { Price }} & \\ \begin{array}{c} \text { Commodities } \\ \text { } \end{array} & \begin{array}{c} \text { Base } \\ \text { year } \end{array} & \begin{array}{c} \text { Current } \\ \text { year } \end{array} & \text { Quantity } \\ \hline \text { Rice } & 32 & 48 & 25 \\ \hline \text { Sugar } & 25 & 42 & 10 \\ \hline \text { Oil } & 54 & 85 & 6 \\ \hline \text { Coffee } & 250 & 460 & 1 \\ \hline \text { Tea } & 175 & 275 & 2 \\ \hline \end{array}\) -
The annual production of a commodity is given as follows :
\(\begin{array}{|c|c|} \hline \text { Year } & \text { Production (in tones) } \\ \hline 1995 & 155 \\ \hline 1996 & 162 \\ \hline 1997 & 171 \\ \hline 1998 & 182 \\ \hline 1999 & 158 \\ \hline 2000 & 180 \\ \hline 2001 & 178 \\ \hline \end{array}\)
Fit a straight line trend by the method of least squares. -
Calculate price index number for 2005 by
(a) Laspeyre’s
(b) Paasche’s methodCommodity 1995 2005 Price Quantity Price Quantity A 5 60 15 70 B 4 20 8 35 C 3 15 6 20 -
Calculate Fisher’s index number to the following data. Also show that it satisfies Time Reversal Test.
Commodity Price in Rupees per unit Number of units Price (Rs.) Quantity (Kg) Price (Rs.) Quantity (Kg) Food 40 12 65 14 Fuel 72 14 78 20 Clothing 36 10 36 15 Wheat 20 6 42 4 Others 46 8 52 6 -
Ten samples each of size five are drawn at regular intervals from a manufacturing process. The sample means ( \(\overset{-}{X}\) ) and their ranges (R ) are given below:
Sample number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 \(\overset {-}{X}\) 49 45 48 53 39 47 46 39 51 45 R 7 5 7 9 5 8 8 6 7 6 Calculate the control limits in respect of \(\overset {-}{X}\) chart. (Given A2 = 0.58, D3 = and D4 = 2.115) Comment on the state of control.
-
In a certain bottling industry the quality control inspector recorded the weight of each of the 5 bottles selected at random during each hour of four hours in the morning.
Time Weights in ml 8:00 AM 43 41 42 43 41 9:00 AM 40 39 40 39 44 10:00 AM 42 42 43 38 40 11:00 AM 39 43 40 39 42 -
From the following data, calculate the control limits for the mean and range chart.
Sample No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Sample Observations 50 51 50 48 46 55 45 50 47 56 55 50 53 53 50 51 48 56 53 53 52 53 48 50 44 56 53 54 49 55 49 50 52 51 48 47 48 53 52 54 54 46 47 53 47 51 51 57 54 52 -
Solve the following assignment problem. Cell values represent cost of assigning job A, B, C and D to the machines I, II, III and IV.
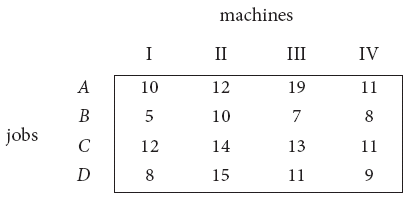
-
A departmental head has four subordinates and four tasks to be performed. The subordinates differ in efficiency and the tasks differ in their intrinsic difficulty. His estimates of the time each man would take to perform each task is given below :
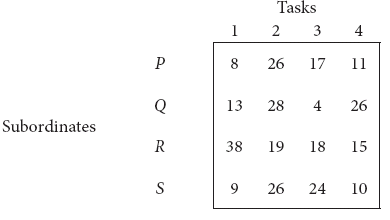
How should the tasks be allocated to subordinates so as to minimize the total man-hours? -
A natural truck-rental service has a surplus of one truck in each of the cities 1,2,3,4,5 and 6 and a deficit of one truck in each of the cities 7,8,9,10,11 and 12. The distance(in kilometers) between the cities with a surplus and the cities with a deficit are displayed below:
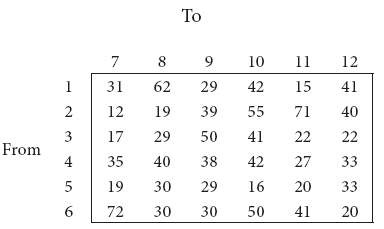
How should the truck be dispersed so as to minimize the total distance travelled?
Part A
48 x 5 = 240
*****************************************
12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Videos
TN 12th Business Maths Applications of Matrices and Determinants 50 Important 1 Marks Questions With
TN Class 12th 2024 Business Maths and Statistics Applications of Matrices and Determinants Study Materials TN State Board / Matriculation 12th Business Maths and Statistics Subject - Applications of Matrices and Determinants One Mark Question and Answers






 12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Syllabus
12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Syllabus  12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Study Materials
12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Study Materials 12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics MCQ Practise Tests
12th Standard Business Maths and Statistics MCQ Practise Tests 

Reviews & Comments about 12th Standard Business Maths English Medium Sample 5 Mark Book Back Questions (New Syllabus 2020)
Write your Comment